
Image credit: frozen Brazilian fruit dessert
What is flash freezing?
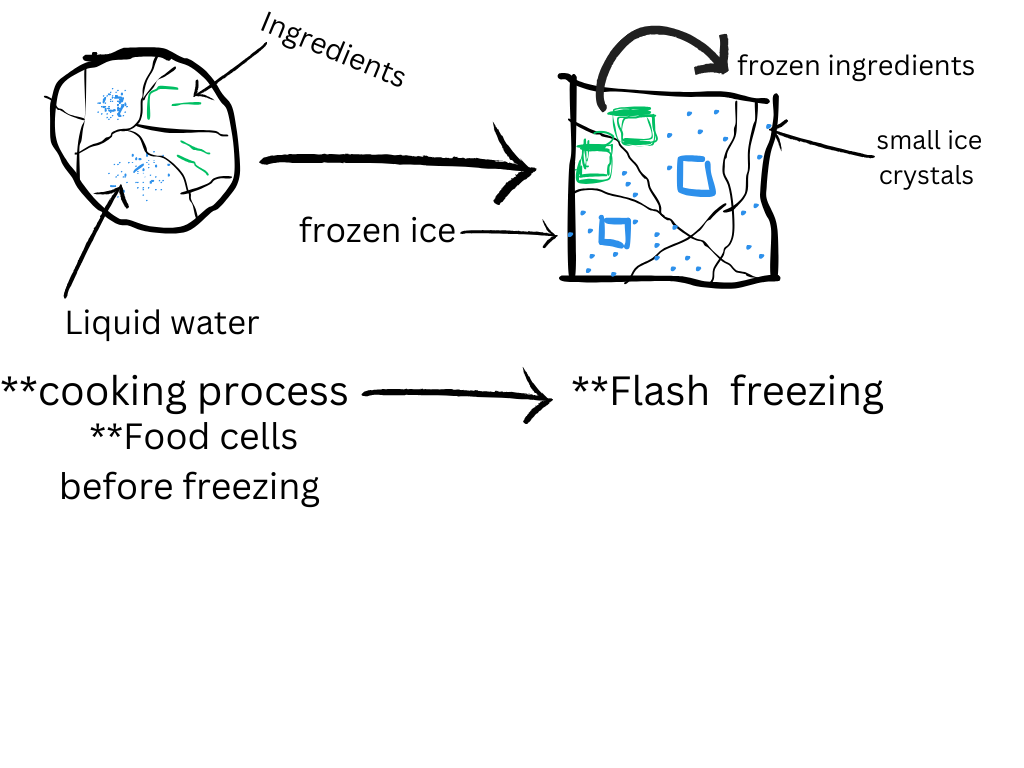
Image created by Canva
The simple definition of flash freezing is lowering temperature—32F or 0C—of food ingredients and keeping the cells in the food or any item intact. The diagram above shows a simple illustration of what happens when food undergoes flash freezing. The ingredients in the food item remain intact while the surrounding solution freezes. Furthermore, this process reduces shipping costs and spoilage because water is frozen in the food item. Another benefit is retention in nutrition content of the final product, such as vitamins and minerals. To note here, ice crystals affect cell integrity over a period of time. As my diagram shows, the cellular structure—before freezing and after flash freezing—has a significant difference. The left diagram illustrates a cell structure that is intact before freezing, while the frozen food item has smaller ice crystals.
Continue reading